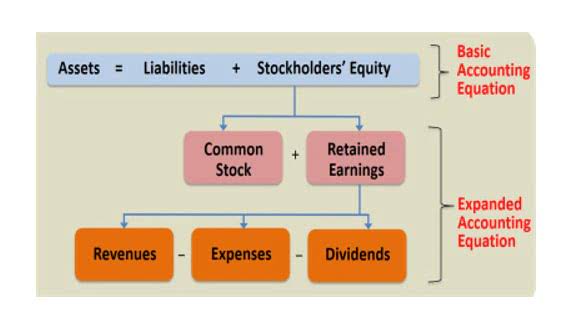
The ownership value of a sole proprietary firm is evaluated after deducting the overall liabilities from the company’s total assets. The Market Capitalization of publicly traded common stock can be construed Travel Agency Accounting as the company’s worth based on its market standing or its demand among investors. This total matches the company’s assets, ensuring the balance sheet is balanced. The stockholders’ equity is only applicable to corporations who sell shares on the stock market.
Impact of Liabilities on Equity
Different types of assets can have varying impacts on a company’s equity. For example, if a company acquires additional assets, such as property or equipment, it may increase its equity position. On the other hand, if a company sells its assets or takes write-downs, it may decrease its equity position. This knowledge empowers you to assess a company’s financial health and potential for total equity formula future growth. Understanding the equity accounting formula is essential for investors because it helps them evaluate the true value of their investments.

These differences affect after-tax returns and influence investor decisions regarding common versus preferred equity. Learn how to calculate common equity, its components, and its role in financial valuation and analysis. The second method involves summing the individual components that make up the equity section of the balance sheet. This approach provides a more detailed breakdown of how total equity is comprised. To calculate total equity this way, you would add Common Stock, Additional Paid-in Capital, Retained Earnings, and Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income, then subtract Treasury Stock. If a company relies too heavily on debt as part of its total capital, it could face debt overhang risk, where the debt becomes unsustainable, leading to financial distress.
How is the Balance Sheet used in Financial Modeling?
This strong equity base helps the company secure investor confidence and fuel future growth. To fully grasp the calculation of common equity, it is essential to understand its components. These elements shape the understanding of a company’s equity position and provide insights into shareholder value. Retained Earnings represent the cumulative net income a company has earned and chosen to keep within the business rather than distribute as dividends. This portion of profits is reinvested into operations, asset acquisition, or debt reduction, contributing to the company’s growth. An increase in retained earnings indicates profitability and financial management.


In closing, the owner’s equity value was derived after considering the initial investment, accumulated profits, withdrawals made by the owner, and the company’s liabilities. Therefore, the net difference between the total assets belonging to a business and total liabilities reflects the concept of owner’s equity. Shareholder equity includes both common and preferred equity, while common equity refers specifically to the ownership of common shareholders. Common equity and preferred equity are both vital components of a company’s capital structure but serve distinct purposes.

Cash Flow Statement: Explanation and Example
- This result reflects the total equity interest held by common shareholders, offering insights into the company’s financial standing.
- This approach provides a more detailed breakdown of how total equity is comprised.
- Total Equity, often referred to simply as “equity,” represents the residual interest in the assets of an entity after deducting liabilities.
- She holds a Bachelor of Science in Finance degree from Bridgewater State University and helps develop content strategies.
- Retained earnings are the company’s accumulated profits not given to shareholders.
The above formula sums the retained earnings of the business and the share capital and subtracts the treasury shares. Retained earnings are the sum of the company’s cumulative earnings after paying dividends, and it appears in the shareholders’ equity section in the balance sheet. The information needed to derive total equity can be found on a company’s balance sheet, which is one of its financial statements. The asset line items to be aggregated for the calculation are cash, marketable securities, accounts receivable, prepaid expenses, inventory, fixed assets, goodwill, and other assets. The liabilities to be aggregated for the calculation are https://baron89.net/rules-of-debit-and-credit-2/ accounts payable, accrued liabilities, short-term debt, unearned revenue, long-term debt, and other liabilities. All of the asset and liability line items stated on the balance sheet should be included in this calculation.
- Understanding total liabilities and equity is essential for evaluating a company’s financial position.
- It is obtained by taking the net income of the business divided by the shareholders’ equity.
- From the point of view of an investor, it is essential to understand the stockholder’s equity formula because it represents the real value of the stockholder’s investment in the business.
- Negative equity is often a sign of financial distress and can indicate the company’s inability to meet its financial obligations.
- Share repurchases can increase the value of remaining shares by reducing supply or prevent hostile takeovers by decreasing available voting power.
- Suppose Company B has $5 million in assets but $4.5 million in liabilities.

If positive, the company has enough assets to cover its liabilities. If negative, the company’s liabilities exceed its assets; if prolonged, this is considered balance sheet insolvency. Typically, investors view companies with negative shareholder equity as risky or unsafe investments.


